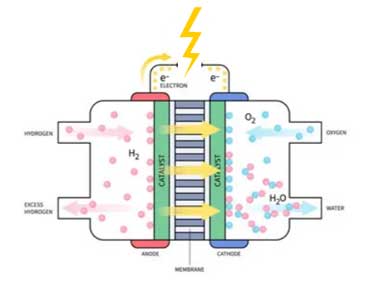
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen Powered Fuel Cell Specification
1. General Description
- Type: Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell
- Application: Suitable for vehicles, stationary power generation, and portable devices.
- Advantages:
- High power density
- Quick start-up
- Low operating temperature
2. Performance Specifications
- Power Output:
- Nominal Power: 5 kW - 100 kW (scalable based on stack size)
- Peak Power: Up to 120% of nominal for short durations
- Efficiency:
- System Efficiency: Approximately 50-60% (LHV - Lower Heating Value)
- Peak Efficiency: Up to 65% under optimal conditions like full load and ideal temperature
- Voltage:
- Nominal Voltage: Variable, typically around 40-60 V per cell stack
- Operating Voltage: 0.6-0.8 V per cell, depending on load and hydrogen quality
- Current Density:
- Max Current Density: 1.5 A/cm², can vary with membrane and catalyst efficiency
- Response Time:
- Startup Time: Cold start less than 30 seconds (from -20°C to operational with pre-heating)
- Load Response: Immediate response to load changes due to quick proton exchange
3. Fuel Specifications
- Hydrogen Quality:
- Purity: ≥99.97% to prevent catalyst poisoning
- Maximum Impurities:
- Water: <5 ppm
- CO: <1 ppm, as it can poison the platinum catalyst
- O₂: <2 ppm
- Other hydrocarbons: <2 ppm
- Fuel Pressure:
- Operational Pressure: 1-5 bar (variable by system design for optimal diffusion)
- Fuel Storage:
- Type IV composite hydrogen cylinders for high-pressure storage
- Liquid hydrogen tanks for larger systems or long-duration storage
4. Environmental & Operating Conditions
- Operating Temperature:
- Cell: 60°C to 80°C for efficient proton exchange
- System: -20°C to 50°C (ambient) with appropriate cooling and heating mechanisms
- Humidity:
- Operating Humidity: 20% to 95% RH, membranes require hydration for conductivity
- Altitude:
- Operational: Up to 2,000 meters without derating, higher altitudes may require pressure adjustments
5. Durability & Lifetime
- Lifetime:
- Expected: >5,000 hours for automotive; up to 40,000 hours for stationary applications
- Degradation Rate: <10 µV/h under normal operation
- Cycling:
- Start/Stop Cycles: >10,000 for automotive applications due to frequent use
6. Physical Specifications
- Dimensions:
- Varies by application; for a 100 kW system, approximately 1 m³ including auxiliaries
- Weight:
- Approximately 50-100 kg per 50 kW (excluding hydrogen storage, varies with materials used)
7. Safety Features
- Hydrogen Leak Detection: Integrated sensors for immediate action
- Thermal Management: Cooling systems to maintain optimal temperature and prevent overheating
- Overpressure Protection: Pressure relief valves and system shutdown capabilities
- Electrical Safety: Compliance with IEC 62282-3-100 for fuel cell systems to ensure no electrical hazards
8. Standards Compliance
- ISO 22734: Hydrogen generators using fuel processing technologies
- ISO 14687: Quality of hydrogen for PEM fuel cells
- IEC 62282: Fuel cell technologies
9. Maintenance
- Service Intervals: Annual inspection recommended; component-specific maintenance as per manufacturer's guidelines
- Maintenance Tasks:
- Replacement of air filters
- Cleaning or replacement of humidifiers
- Inspection of electrical connections
10. Environmental Impact
- Emissions: Water vapor as primary byproduct; zero CO2 emissions during operation, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions